ICSI is an advanced fertility treatment for male infertility. This gives best success in the hands of expert IVF doctors and embryologists. Your doctor will suggest ICSI for many reasons as well as better success. Even if you have severe defects of sperm, this wil give you a successful pregnancy. Although sperm selection requires highly skilled professional, this treatment offers hope to people with severe male factor. In comparision to conventional IVF treatment, ICSI gives better pregnancy rates.
What is ICSI ?
While doing ICSI the embryologist chooses a single healthy sperm cell. He injects this sperm cell directly into the cytoplasm of an egg. Injecting sperm through the egg’s shell helps the sperm to fertilize. This way it directly bypasses the need to penetrate the shell. While doing ICSI your embryologist can record the whole process so that you can see the quality of egg and sperm. Sometimes, the egg has a thick covering which prevents sperm to enter on its own. In case, you have PCOS or unexplained infertility ICSI will overcome the obstacle.
When ICSI treatment is suggested?
These are few conditions where your doctor will prefer ICSI treatment over IVF. Before your fertility treatment she will explain each and every step. In addition, you can opt to see the procedure live. These are few conditions where you will require this procedure
- Teratozoospermia
- Azoospermia
- Oligozoospermia
- Asthenozoospermia
- Immunological factors (antisperm antibodies)
- Testicular cancer
- Frozen semen sample
- Previous failure IVF attempts
- Sperms retrieved by surgical techniques(TESA, PESA, MESA,TESE)
- Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis
Pre ICSI workup
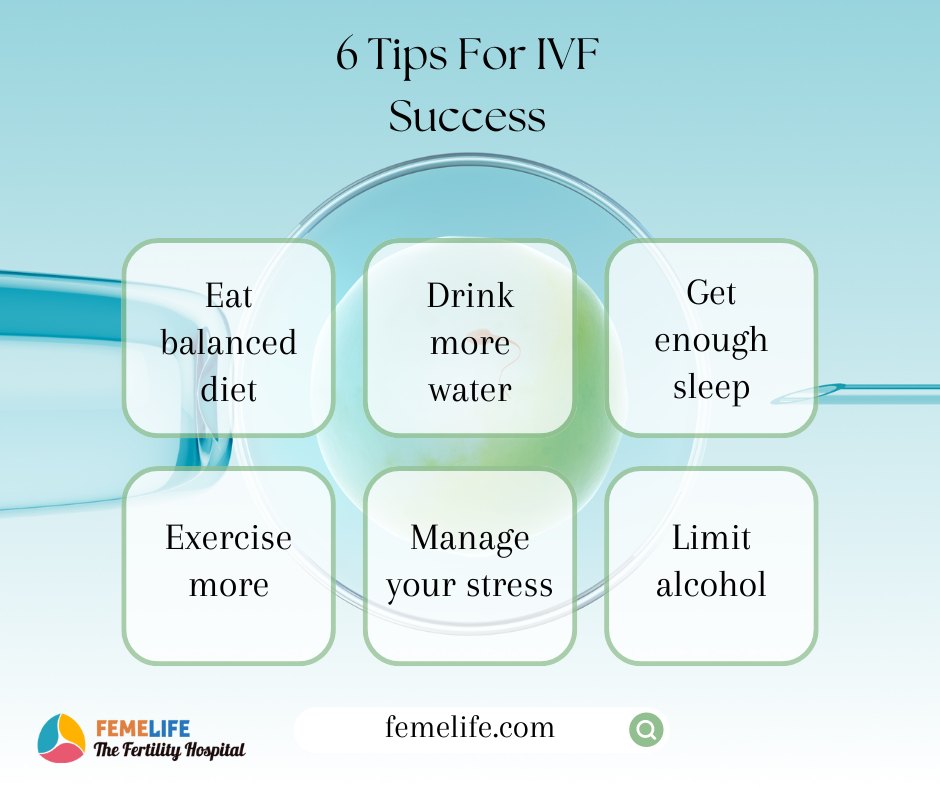
Your doctor will suggest medications for few months to improve quality of eggs and sperm. Although you may feel deperate during your treatment, please go though each step patiently. She will suggest lifestyle modifications for better success. Also, she will regulate your menstrual cycle with medications. Hormones play a variety of roles in IVF process. Hence follow a healthy lifestyle to achieve success. There are several procedure to follow before extracting eggs for ICSI.
- Ovarian Stimulation
- Monitoring
- Ovulation Induction
- Oocyte retrieval
- Semen collection & preparation
What are the procedures after ICSI?
- ICSI
- Embryo development
- Implantation or Cryopreservation
What you should know before ICSI treatment?
Couples wishing to undergo (ICSI) need counselling before commencement of treatment. Hence attend the sessions regularly to clarify any concerns. You will know the entire procedure and its outcome by discussion with your specialist.
You must know that ICSI is not a sure success getway to pregnancy. In fact at may instances it fails to get embryos for transfer. Hence, do discuss alternative options (e.g. use of donor sperm, adoption) in case of a failure. In addition, couples undergoing (ICSI) should be aware of and discuss the increased risk of congenital abnormalities, particularly in male offspring.
Simulating follicles and retrieving eggs
Ovarian stimulation (agonist/antagonist) can be done by any of the ways
- Short/mild protocol
- Long/standard protocol
- Ultra short/modified protocol
Hormonal treatment to stimulate the ovaries produces several eggs. Monitoring the follicular growth and count by ultrasound scanning is done by your fertility specialist.
The process of egg retrieval
This process happens after 34-36 hours of the hCG trigger
It is a laparoscopic surgery guided by the ultrasound
The mature ovarian follicles are drained; the follicular fluid is sent to the lab to locate the oocytes under analgesia or anesthesia. Aspiration- aspirating needle inserted into the follicle to aspirate the follicular fluid containing oocyte/OCC by applying suction.
Sperm Preparation
- Semen collection and preparation
- Frozen donor sperm can also be used after matching
- Semen preparation by density gradient or swim up method
ICSI Procedure
After oocyte retrieval your embryologist identifies the of oocytes in the follicular fluid.
The embryologist will denude of the oocytes and separate the mature eggs.
- She prepares the ICSI dish before starting the process.
- The mature egg is held with a holding pipette.
- A very sharp and hollow needle is used to immobilize and pick up a single sperm.
- This needle is then inserted through the zona and in to the center (cytoplasm) of the egg.
- The sperm is injected by aspirating some of the cytoplasm along with the sperm and releasing them back. Injected eggs are placed in CO2 incubator.
- The eggs are checked for fertilization after 22 hrs.
Advantages of ICSI Treatment
It provides the male partner an opportunity to father a child using his own sperm.
Couples can also go for ICSI before Opting to donor sperm for viable sperms.
ICSI can be performed even if the man has undergone a vasectomy. In that case, viable sperm can be extracted directly from testicles using special sperm retrieval techniques and injected into the egg
Disadvantages
- Damage to the embryos
- Multiple pregnancies
- Invasive
- Risk of OHSS (stimulation)
- Birth defects
Fertilization and pregnancy success with ICSI Treatment
The ICSI procedure fertilizes 50 to 80 percent of eggs.
Success is 35% in women aged 30 to 35, 20% at 35 to 40, and less than 10 % after 40.
Blastocyst embryo transfer at the 5–6-day stage, generally has higher success rates than embryo transfer at the 2–3-day stage.
Depending on the age of the couple, hormone levels, disease (Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, etc.) and lifestyle (excess weight, stress, alcohol and nicotine use, etc.)
the average egg quantity and quality tends to be better in ICSI cases (male factor cases) because it is less likely that there is a problem with the eggs – as compared to cases with unexplained infertility. Some unexplained cases have reduced egg quantity and/or quality – which lowers the chances for a successful IVF outcome.




Also read